ABSTRACT
These Whisper Studies demonstrate two initial uses cases that prompted organizations to add data virtualization to their architecture. The first study involves a North American-based railroad’s evolution to Precision Railroading, which required entirely new operational metrics. To develop the metrics, the team required replica of production without affecting production. The railroad leveraged Teradata QueryGrid. The second study is from a consumer electronics manufacturer that wished to reduce its cost basis for data storage and computation. The original application did not require any changes. The manufacturer leveraged Gluent on Oracle and Hadoop to achieve their desired result.
The Studies
Railroad Access On-Premise Data
- Scenario: Production data in Teradata – needed parallel dev environment
- Start State: Production data in Teradata Active Enterprise Data Warehouse
- End State: Teradata QueryGrid provides data access to dev environment
- Data Size: 5 terabytes
- Set-up Time: Half day to install, 6 months to optimize tuning
- Interview(s): August 2019
Consumer Products Manufacturer to Lower Cost Performance Data Management
- Scenario: Application leverage Oracle production database
- Start State: Oracle storage growing too fast, too expensive
- End State: Leveraged Gluent to evolve data and computations to Hadoop
- Data Size: 31 terabytes of application data in Oracle Database
- Set-up Time: One-hour installation, two months to implement
Interview(s): March 2020
Key Takeaways
- Data virtualization is frequently brought into environments to provide access to production data without disturbing the production environment.
- Data virtualization is frequently brought into environments to reduce the cost structure of an environment. Data virtualization is also useful in bringing legacy applications into a modern data management solution.
- Set up for data virtualization is often quick; initial set up frequently takes less than a day, while most organizations become fluent in tuning the environment within 2-6 months.
Data Virtualization Use-Case Studies
These Whisper Studies center on two cases leveraging a data virtualization platform. In both scenarios, it is the organization’s first data virtualization use case or the one that caused them to add it to their architecture. The first study involves an organization that needed to update its operational models and related analytics. They needed to leverage production data to develop and confirm new metrics without disrupting production. The second Whisper Study wished to reduce the cost profile of their production and analytics without a major architecture change. Both leveraged data virtualization to address their needs.
A North American Railroad’s Parallel Production Data Environment
- Scenario: Production data in Teradata – needed parallel dev environment
- Start State: Production data in Teradata Active Enterprise Data Warehouse
- End State: Teradata QueryGrid provides data access to Dev
- Data Size: 5 terabytes
- Set-up Time: Half day to install, 6 months to optimize tuning
- Interview(s): August 2019
A North American-based railroad company needed to move to new operational analytics as part of moving toward Precision Schedule RailRoading1. To accomplish this, the railroad wanted to evaluate the new operational metrics in development before updating production.
Precision Railroading Background
To evaluate the new metrics, the organization required a parallel environment to that of production. This parallel environment required some 30 tables and millions of rows of data – all without interrupting or burdening production. The data was primarily transportation data with some finance data mixed in.
To accomplish this, development needed an exact copy of the large volumes of production data. The copy needed to be scheduled, properly updated based on all dependent processes, and the development copy needed to be complete. In addition, to compare the new set of operational metrics to the current operational models, target tables of production were also required in the parallel environment.
Note that as a railroad is land rich with significant bandwidth available along the lines, the railroad owns and operates two of its own data centers. This also allows the organization to control the highly sensitive data regarding its operations that affect multiple industries, since they ship raw ingredients across the continent. As such, their entire solution is considered on-premise.
Teradata QueryGrid Solution
Because a majority of the data was in Teradata Active Enterprise Data Warehouse on-premise, it was natural to reach out to Teradata for a solution, which provided Teradata QueryGrid2, a data virtualization solution. Additional research that provides details on QueryGrid’s capabilities can be found in “Whisper Report: Six Data Engineering Capabilities Provided by Modern Data Virtualization Platforms.”
By leveraging QueryGrid, the railroad had a perfect replica of production without the concern of interfering with production. When using a data virtualization platform, the platform provides a view of the data to execute your needs. This view is independent of the original form of the data but may or may not actually involve an additional complete physical copy of the data. More importantly, the data virtualization technology is able to maintain an up to date view of the data, as depicted in Figure 1.
The Set-Up
To leverage Teradata’s QueryGrid, the following steps were required.
Connect the source: As with all data layers, the specific sources to be used by the platform must be connected. When connecting the sources, the majority of the time was spent tracking down and setting up the permissions to connect.
Configure the views: Data virtualization platforms such as QueryGrid operate by providing data views. The second step was creating the required data views as required for the Precision Railroading Project.
To protect production, only official DBAs within IT could create views leveraging QueryGrid – they did not want production data to be wrongly exploited. No major problems were incurred by the project.
Figure 1. Develop with Production Data without Affecting Production
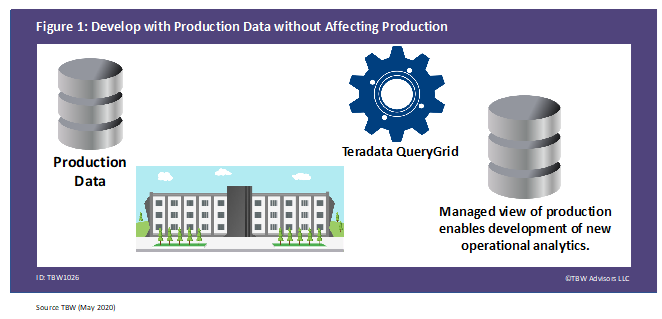
The Results
With the exact replica of production data and related current operational metrics, the railroad was able to perform a side-by-side comparison with the incoming Precision Railroading Metrics. It was critical for the business to get comfortable with the impact of the new metrics before they became the official operating metrics for the company. Accuracy was critical, as the railroad’s operational metrics are publicly released. Note, formal data validation platforms were not used to compare the data, but rather, SQL scripts were leveraged (see Whisper Report: Decision Integrity Requires Data Validation for related research).
The new corporate reporting metrics tracked events such as how long a train took to go from Point A to Point B, as well as how long the train stayed or stopped at each of the stations between the two points. Overall, there were an assortment of metrics that are part of the Precision Railroading that they wanted to realize. As a result of the new operational insights, they found numerous opportunities to make improvements in the process. For example, visibility was given to instances where certain customers required multiple attempts to successfully deliver a load. With the waste identified, the organization could now address issues that negatively impacted their efficiencies.
This project was the railroad’s first Teradata QueryGrid project. With success under their belt, the next project will expand the business’s ability to be more involved in self-service.
Consumer Electronics Manufacturer Reducing Cost Profile
- Scenario: Application Leverage Oracle Production Database
- Start State: Oracle Storage Growing Too Fast, Too Expensive
- End State: Leveraged Gluent to seamlessly evolve older data to Hadoop
- Data Size: 31 terabyte of application data in Oracle Database
- Set-up Time: One hour to install, two months to implement
- Interview(s): March 2020
Background on Reducing the Cost Profile
The second study involves a large electronics manufacturer seeking to reduce their cost profile. The electronics manufacturer has a large amount of sensor data coming from their machines (a single data set is 10 terabytes). The data regarding the machines is stored in an Oracle database, which worked well at first but was not able to maintain the cost profile desired by the organization. There was an annual expense for additional space required in order to continue leveraging the application storing information in Oracle. This organization wished to reduce the cost profile without rewriting the application.
The Gluent Solution
The consumer electronics manufacturer decided to leverage Gluent data virtualization solution3. Gluent was installed on the Oracle server and Hadoop. The application simply connected to Oracle without any changes whatsoever. Behind the scenes, the data and the work on the data was now spread between Oracle and Hadoop significantly reducing their cost structure and eliminating the need for the organization to expand their Oracle footprint. The fact that the data was spread between Oracle and Hadoop was invisible to the application and its users, as depicted in Figure 2.
The Set-Up
In order to leverage Gluent the following steps were required.
Install Gluent: Gluent is installed on all data sources, particularly Hadoop and Oracle. When Oracle or Hadoop is called today, users are actually using the Gluent code installed on the server. The work is now able to be seamlessly offloaded to Hadoop as needed and is cost optimized. The install took less than one hour. Once again, it is critical to have access passwords available. Setting permissions correctly is also required.
Use the migration tool: Gluent has a built-in migration tool the consumer manufacturer was able to leverage to handle the initial set up. This automatically migrated some of the Oracle data to Hadoop while maintaining a single view of the data.
Query Tune: This is a continual effort that gets easier over time. When optimizations turn out to not be optimal, Gluent allows “Hints,” which are the methods one can design to optimize specific scenarios.
Figure 2. Gluent is Used to Extend Oracle Data to Hadoop Reducing Cost
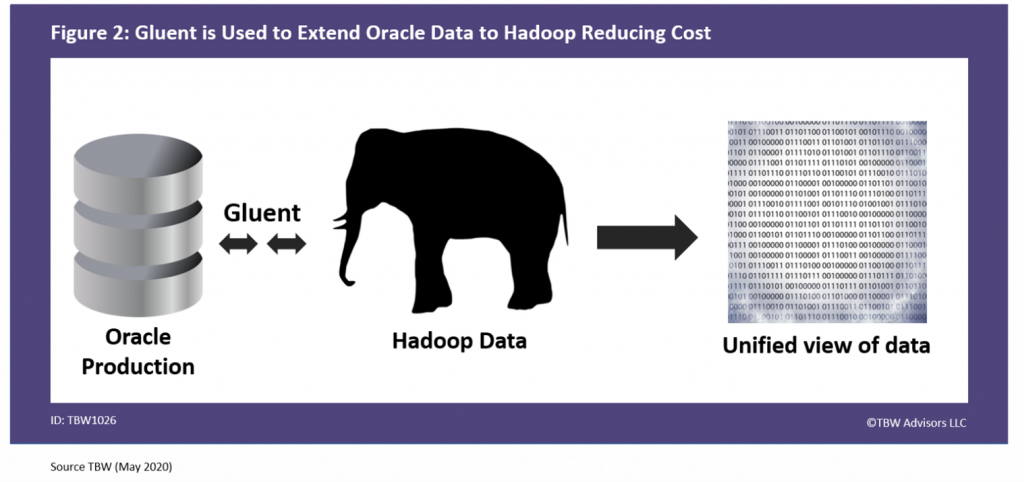
The Results
The Oracle Applications still call on and use Oracle. Behind the scenes, Gluent installed on Oracle is able to leverage Hadoop for storage and compute power. The application itself did not require any changes. Their cost profile for data storage and computations is now reduced. The plan is to not change the Oracle application at all but, rather, to simply continue reducing the actual data and computations conducted by Oracle. Fortunately, this also moved this application group in line with other internal groups that are using big data solutions on Hadoop. The Hadoop environment is familiar to the other teams, and through Hadoop due to Gluent, those users can now leverage the Oracle application and related data without Oracle skills. This capability is due to two functionalities that are common in data virtualization.
Remote Function Execution: The ability of data virtualization to parse a query and have portions of a query executed on another remote system. In this instance, one can access Oracle and run the query on Hadoop. Likewise, one can access Hadoop and have a query run on Oracle. Where a query runs is subject to configuration and constraints such as cost and time.
Functional Compensation: The ability perform an Oracle operation, specifically SQL, on your Hadoop data, even though Hadoop does not support SQL queries natively.
Together, these two capabilities enable the manufacturer to leverage their Oracle experts without retraining. This benefit is in addition to reducing their storage and computational costs.
TBW Advisors Recommended Reading
“Whisper Report: Digital Transformation Requires Modern Data Engineering”
“Whisper Report: Six Data Engineering Capabilities Provided by Modern Data Virtualization Platforms”
“Whisper Report: Six Use Cases Enabled by Data Virtualization Platforms”
“Whisper Ranking: Data Virtualization Platforms Q1 2020”
“Whisper Report: ETL Not Agile? Here’s 3 Alternatives”
“Whisper Report: Decision Integrity Requires Data Validation”
Citations
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Precision_railroading
- https://www.teradata.com/Products/Ecosystem-Management/IntelliSphere/QueryGrid
- https://gluent.com/
Corporate Headquarters
2884 Grand Helios Way
Henderson, NV 89052
©2019-2020 TBW Advisors LLC. All rights reserved. TBW, Technical Business Whispers, Fact-based research and Advisory, Conference Whispers, Whisper Reports, Whisper Studies, Whisper Ranking are trademarks or registered trademarks of TBW Advisors LLC. This publication may not be reproduced or distributed in any form without TBW’s prior written permission. It consists of the opinions of TBW’s research organization which should not be construed as statements of fact. While the information contained in this publication has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable, TBW disclaims all warranties as to the accuracy, completeness or adequacy of such information. TBW does not provide legal or investment advice and its research should not be construed or used as such. Your access and use of this publication are governed by the TBW Usage Policy. TBW research is produced independently by its research organization without influence or input from a third party. For further information, see Fact-based research publications on our website for more details.